Facility Maintenance | April 27, 2023
Prioritizing Maintenance and Repair for Preserving Asphalt Pavement
Why It Matters
Regular pavement maintenance and repair activities can preserve your pavement for 30 to 40 years at a significantly lower cost than replacing it when it fails, affording you a flat operating budget in lieu of deferred capital liability.
The Full Story
Asphalt pavement provides a smooth and safe driving surface for millions of people around the world. However, over time, asphalt pavements are subjected to various forms of wear and tear, including weathering, traffic loads, and aging, which can lead to cracks, potholes, and other forms of deterioration.
To extend the lifespan and performance of asphalt pavements, low-cost preservation techniques such as patching, joint and crack sealing, and mill and overlay can extend pavement life and cost far less than a full-depth replacement. In this blog post, we explore the benefits of these asphalt pavement preservation techniques and how they can enhance the durability and performance of road surfaces.
Patching
Patching is a common asphalt pavement preservation technique that involves repairing localized areas of the pavement that have deteriorated due to fatigue cracking, potholes, or other forms of damage. Patching is typically done using asphalt materials that are similar in composition to the existing pavement, ensuring a seamless and durable repair.
One of the key benefits of patching is that it addresses localized pavement damage promptly, preventing it from spreading and causing further deterioration. Cracks and potholes can allow water to penetrate the pavement, leading to accelerated deterioration and increased repair costs. By patching these areas, water infiltration is minimized, protecting the underlying pavement layers and extending the pavement's service life.
Another advantage of patching is that it helps to maintain a smooth driving surface, reducing the potential for vehicle damage and improving the ride quality for road users. Potholes and cracks can create uneven surfaces that can be uncomfortable for drivers and cause premature wear and tear on vehicles. Patching restores the pavement's smoothness, reducing the risk of accidents, and ensuring a safer driving experience.
Crack Sealing
Crack sealing is a preventive maintenance technique that involves filling or sealing cracks in the pavement to prevent water infiltration and further pavement damage. Cracks are unintentional distress that develops in the pavement due to various factors such as temperature changes, traffic loads, and aging.
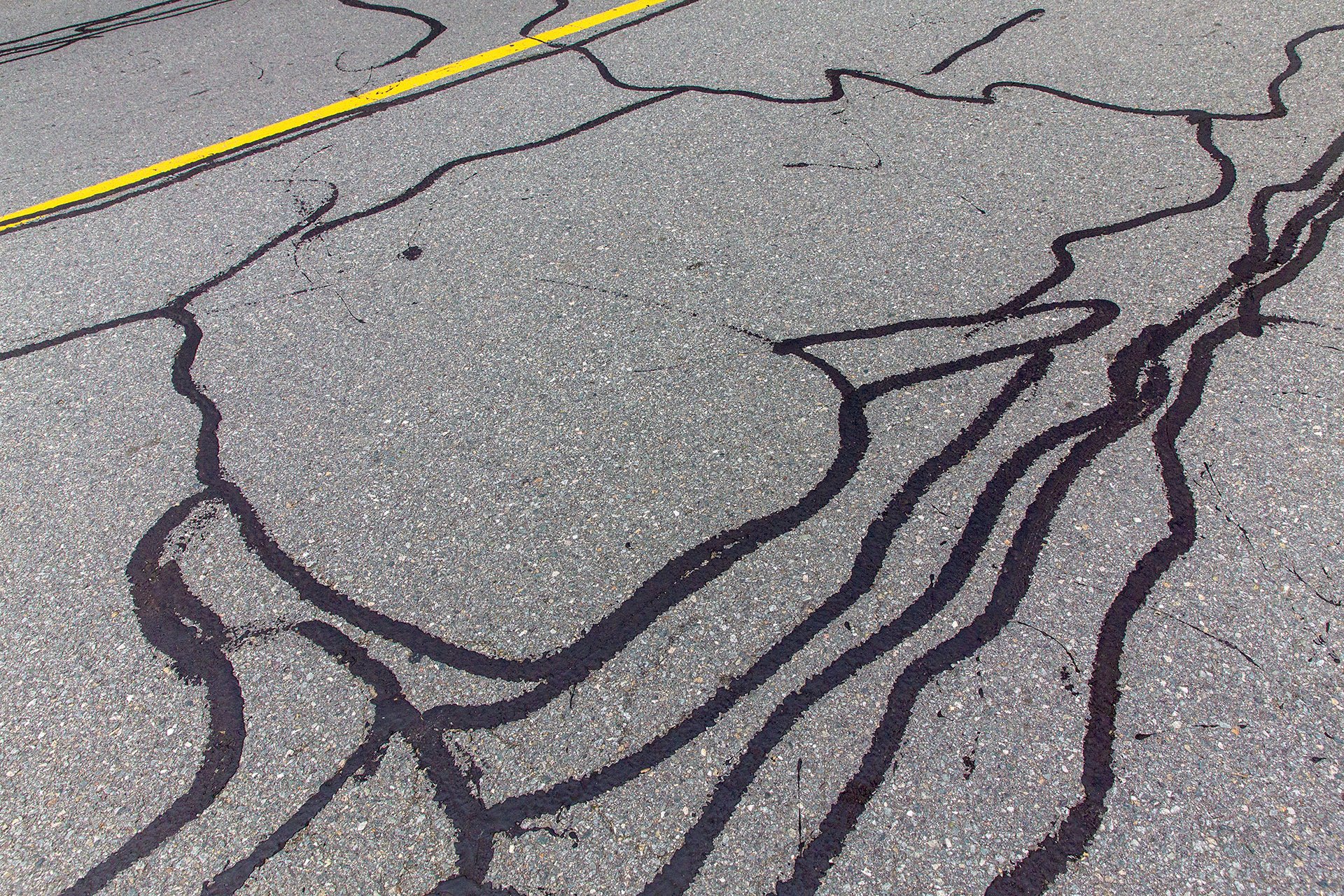

One of the key benefits of crack sealing is that it prevents water from penetrating the pavement, which is a major contributor to pavement deterioration. Water can infiltrate through cracks, leading to the erosion of underlying pavement layers and causing potholes, raveling, and other forms of damage. Crack sealing helps to keep water out, protecting the pavement structure and extending its lifespan.
In addition to preventing water infiltration crack sealing also helps to reduce the risk of further pavement damage. By sealing the cracks, the entry of debris, dirt, and other harmful substances into the pavement is minimized. This helps to prevent the accumulation of debris in the cracks which can lead to further pavement damage and compromise the pavement's structural integrity.
Mill and Overlay
Mill and overlay, also known as resurfacing, is a pavement preservation technique that involves removing the top layer of the existing pavement and applying a new layer of asphalt on top. Milling is the process of removing the deteriorated pavement surface using specialized milling equipment, while overlaying is the application of a new layer of asphalt on the milled surface.
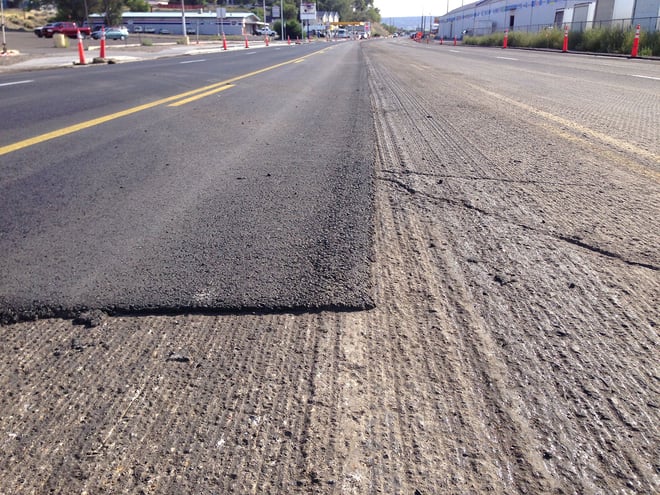

One of the key benefits of mill and overlay is that it restores the pavement's smoothness and improves its ride quality. Over time, asphalt pavements can develop surface defects such as ruts, potholes, and cracks that can make the driving experience uncomfortable, potentially damaging to vehicles, and create trip hazards. Milling the deteriorated surface and applying a new overlay provides a fresh and smooth driving surface, improving ride quality, reducing wear and tear on vehicles, and improving aesthetics at a facility.
Another advantage of mill and overlay is that it adds a new layer of protection to the pavement, extending its lifespan. The new overlay acts as a barrier against water infiltration, preventing moisture from reaching the underlying pavement layers and causing further damage. It also adds structural integrity to the pavement, improving its load-carrying capacity and overall performance.
Mill and overlay is also a cost-effective pavement preservation technique compared to full-depth replacement. Removing and replacing only the top layer of the pavement is less expensive than reconstructing the entire pavement structure, saving time and resources. It also minimizes disruptions to traffic and reduces the overall downtime of the road during construction, making it a convenient option for pavement preservation.
Full-Depth Replacement
Full-depth replacement is a pavement preservation technique that involves removing the entire existing pavement structure, including the base and subbase layers, and replacing it with a new pavement section. This technique is typically used when the existing pavement severely deteriorates or when the pavement's structural integrity has been compromised.
One of the key benefits of full-depth replacement is that it provides a long-term solution for heavily deteriorated pavements. When the pavement has reached a point where patching, sealing, or overlaying is not sufficient, full-depth replacement may be necessary to restore the pavement's structural integrity and performance. The new pavement section provides a fresh and stable foundation for the road, ensuring its durability and longevity.
Another advantage of full-depth replacement is that it allows for the correction of underlying issues that may have caused pavement deterioration. If the base or subbase layers are compromised due to inadequate design, poor drainage, or other factors, full-depth replacement provides an opportunity to address these issues and ensure proper pavement performance in the long term.
Full-depth replacement also allows for improvements in the pavement's design and functionality. It provides an opportunity to modify the pavement structure to better accommodate changing traffic patterns, heavier loads, or other evolving needs. This can result in a more durable and resilient pavement that can better withstand the demands of modern transportation.
In Conclusion
Asphalt pavement preservation techniques such as patching, joint and crack sealing, and mill and overlay offer numerous benefits in enhancing the durability and performance of road surfaces at a lower cost than full-depth replacement. These techniques address localized pavement damage, prevent water infiltration, restore smooth driving surfaces, and extend the lifespan of pavements. They are also cost-effective and minimize disruptions to traffic during construction.
Choosing the right preservation technique depends on the extent of pavement deterioration, structural integrity, and overall goals for the road. Consulting with pavement preservation experts can help determine the most suitable technique for a specific pavement condition, ensuring well-maintained and long-lasting pavements for the benefit of employees and guests.
Related Posts
Discover more content and insights from Mantis Innovation

How Your Pavement Can Reduce Trip, Fall, & Slip Claims
This is the third and final installment in a series of pavement-related pieces that can keep Facilities Management on top of seasonal concerns with asphalt and concrete. While building owners and

Concrete Curing 101: Understanding a Critical Step in Your Pavement Projects
This is the second in a series of pavement-related pieces that can keep Facilities Management on top of seasonal concerns with asphalt and concrete. While building owners and operators are

The Heat is On: Strategies for Concrete Pavement Longevity Amid Extreme Weather
This is the first in a series of pavement-related pieces that can keep Facilities Management on top of seasonal concerns with asphalt and concrete. For many building owners and operators, pavement
Oh, Hail No: Roofing Tips for Severe Weather Season
Even a minor hailstorm can compromise your commercial roof’s integrity, making it essential to conduct a thorough inspection after any such event. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric